Movie
ECHONET CONSORTIUM
Promotion Video
(YouTube)
ECHONET is a communication protocol designed to create the “smart homes” of the future. Today, with Wi-Fi and other wireless networks readily available in ordinary homes, there is a growing demand for air-conditioning, lighting and other equipment inside the home to be controlled using smartphones or controllers, or for electricity usage to be monitored in order to avoid wasting energy.
To achieve this kind of low-energy, comfortable, safe and reassuring lifestyle, we first need to create a system of rules or a “communication protocol” that can be read by any manufacturer’s equipment. This is where ECHONET comes in.
The ECHONET Lite specification, in particular, is a communication protocol compatible with the now ubiquitous Internet. It is designed for ease of use and is simpler than the ECHONET specification.
The ECHONET Lite specification is already compatible with more than 100 types of device, and is also being adopted by the smart electric energy meters that will be installed in all households in future.
Introduction of ECHONET (8 min.)
After reaching a peak in FY2004, the energy consumption in Japan has been on a downward trend. This is due to economic growth while curbing energy consumption as Japanese energy consumption moves towards energy saving, particularly in the industry sector, and the development of energy saving products has become popular.
However, when looking at trends by sector for growth between FY1973 (at the time of the oil embargo) and FY2020, while the commercial and business sector remained at 0.9 times with the progress in energy saving mainly in the manufacturing industry, as a result of the 1.9 times increase in energy consumption in the household sector, its share against the total consumption has changed from 8.9% to 15.8%.
In response to the tight power supply and instability of energy prices, there is a renewed sense of the importance of energy conservation in the household sector and it is essential to improve the energy conservation of houses themselves.
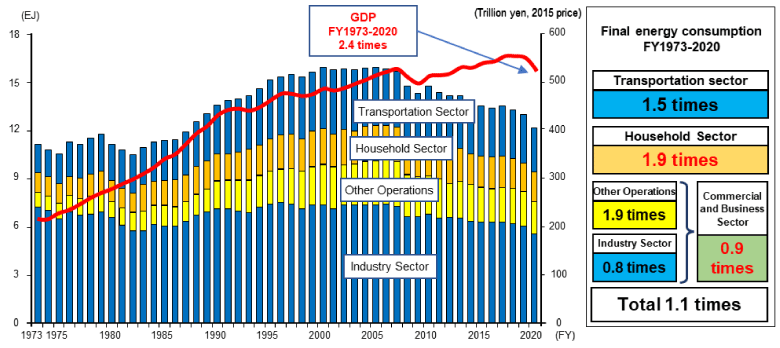
Source: Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry / Agency for Natural Resources and Energy–Japan’s Energy White Paper 2022
On the other hand, thanks to a policy established to promote the introduction of solar power generation, it has increased by an average of approximately 64 MW a month since 2013 and is forecast to reach approximately 140 GW by 2030. The result of this may cause that the generated power has exceeded demand from business offices and homes is flowing into the power distribution system and as this has caused a rise in voltage in the power distribution system, it has the potential to interrupt the high quality and stable provision of power. In order to prevent this, in addition to promoting technical development that would restrain the amount of power generated by solar power generation, there are calls for promoting the deployment of equipment that can store energy, such as electric vehicles, storage batteries and heat pump water heaters, thus “creating electricity”, “storing electricity” and “efficiently using electricity”.